Is Light Microscope And Electron Microscope Same Introduction People and other animals can see because there is light Light is a form of energy The Sun is a very important source of light energy Without the energy from the Sun there would be no plants or animals on Earth s surface
In the mid 19th century light was described by James Clerk Maxwell in terms of electromagnetic waves but 20th century physicists showed that it exhibits properties of particles as well its carrier particle is the photon Light is the basis for the sense of sight and for the perception of colour See also optics wave particle duality Jul 28 2025 0183 32 Light Reflection Refraction Diffraction The basic element in geometrical optics is the light ray a hypothetical construct that indicates the direction of the propagation of light at any point in space The origin of this concept dates back
Is Light Microscope And Electron Microscope Same
 Is Light Microscope And Electron Microscope Same
Is Light Microscope And Electron Microscope Same
https://i.ytimg.com/vi/Yw38VpkQ7wI/maxresdefault.jpg
Aug 21 2025 0183 32 Light pollution is unwanted or excessive artificial light It is a form of waste energy that can have adverse effects on birds and other migratory animals and degrade environmental quality
Templates are pre-designed files or files that can be used for various purposes. They can conserve effort and time by offering a ready-made format and layout for developing different type of content. Templates can be utilized for individual or expert jobs, such as resumes, invites, flyers, newsletters, reports, discussions, and more.
Is Light Microscope And Electron Microscope Same

Difference Between Light And Electron Microscope Microscope Crew
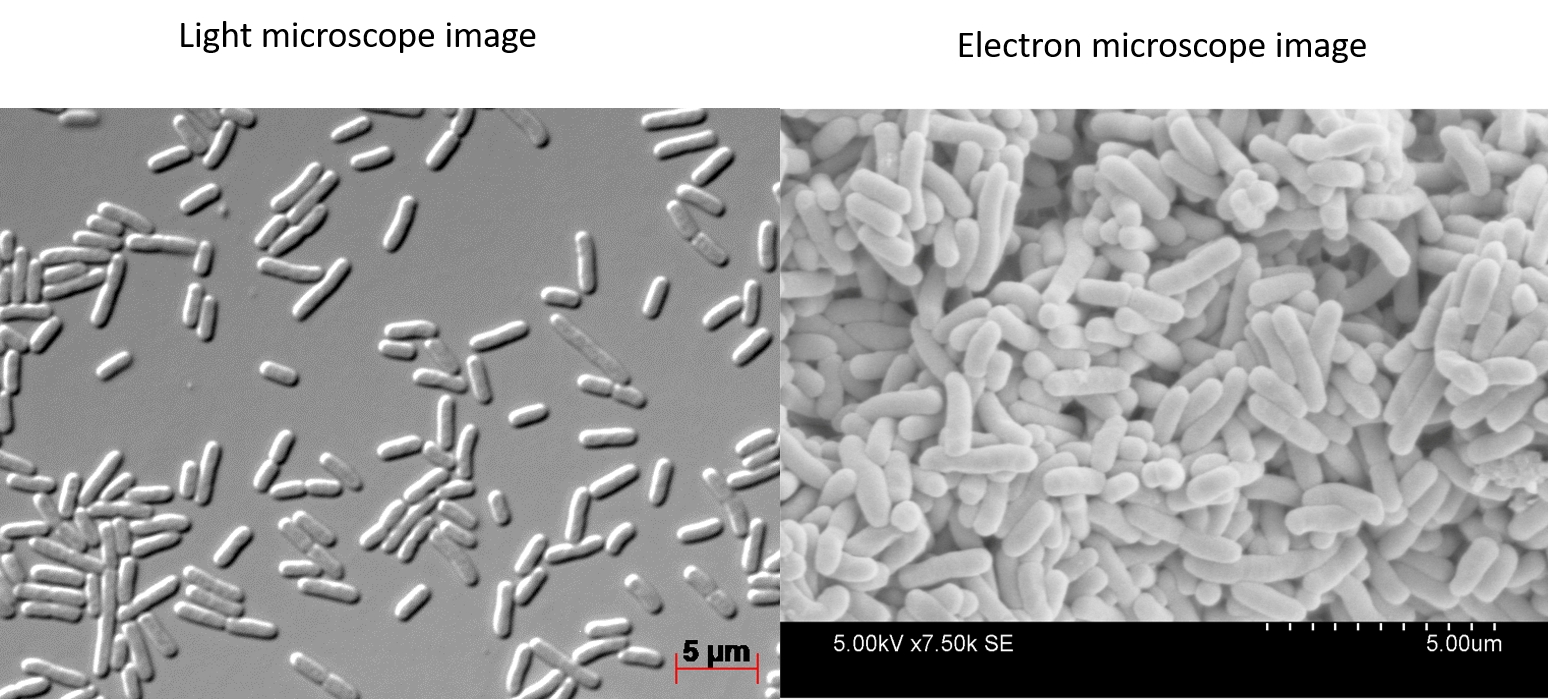
Bacteria Under A Light Vs Electron Microscope SciTales
Physics Shining Light On Electron Microscopy
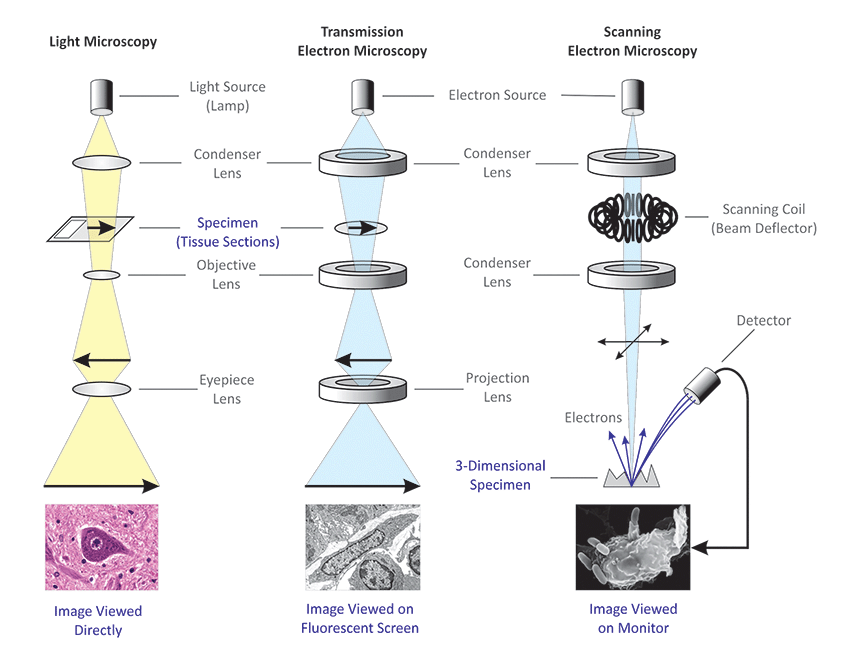
Differences Between Light Microscope And Electron Microscope
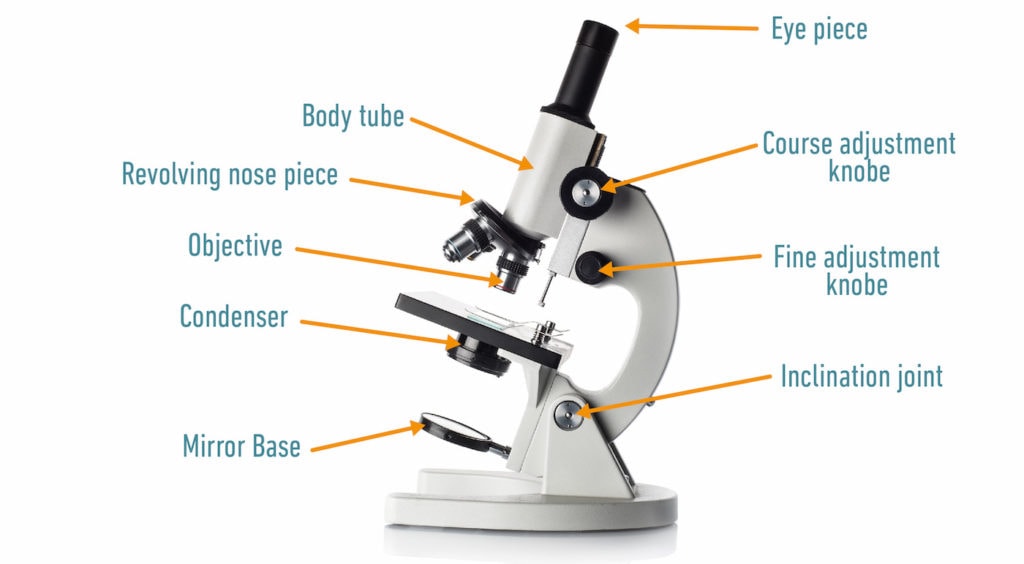
Distinguish Between Light Microscope And Electron Microscopy
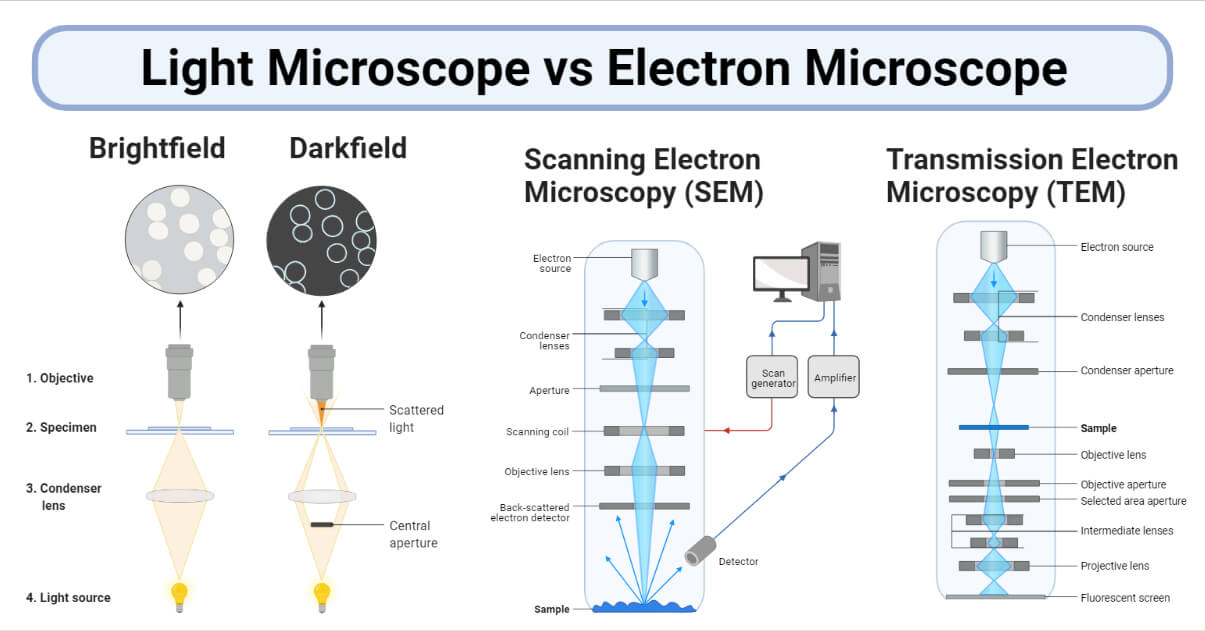
Light Microscope Vs Electron Microscope 36 Major Differences

https://www.britannica.com › science › light › Light-as-electromagnetic-r…
Jul 28 2025 0183 32 In his formulation of electromagnetism Maxwell described light as a propagating wave of electric and magnetic fields More generally he predicted the existence of electromagnetic radiation coupled electric and magnetic fields traveling as waves at a speed equal to the known speed of light

https://www.britannica.com › science › light › Characteristics-of-waves
Jul 28 2025 0183 32 Light Wavelength Frequency Amplitude From ripples on a pond to deep ocean swells sound waves and light all waves share some basic characteristics Broadly speaking a wave is a disturbance that propagates through space

https://kids.britannica.com › students › article › light
Light sources are necessary for vision An object can be seen only if light travels from the object to an eye that can sense it When the object is itself a light source it is called luminous Electric lights are luminous The Sun is a luminous object because it is a source of light

https://www.britannica.com › science › light › Reflection-and-refraction
Jul 28 2025 0183 32 Light rays change direction when they reflect off a surface move from one transparent medium into another or travel through a medium whose composition is continuously changing

https://www.britannica.com › science › light › Quantum-mechanics
Jul 28 2025 0183 32 The behaviour of light cannot be fully accounted for by a classical wave model or by a classical particle model These pictures are useful in their respective regimes but ultimately they are approximate complementary descriptions of an underlying reality that is described quantum mechanically
[desc-11] [desc-12]
[desc-13]