What Are Elimination Reaction Give Example E2 elimination reactions in the laboratory are carried out with relatively strong bases such as alkoxides deprotonated alcohols OR 2 Bromopropane will react with ethoxide for example to give propene Propene is not the only product of this reaction however the ethoxide will also to some extent act as a nucleophile in an S 2 reaction
Jan 23 2023 0183 32 E2 bimolecular elimination was proposed in the 1920s by British chemist Christopher Kelk Ingold Unlike E1 reactions E2 reactions remove two subsituents with the addition of a strong base resulting in an alkene Elimination Reactions A Elimination from 2 Bromopropane B Elimination from Unsymmetrical Halogenoalkanes C Jul 12 2023 0183 32 In many cases an elimination reaction can result in more than one constitutional isomer or stereoisomer The elimination products of 2 chloropentane provide a good example This reaction is both regiospecific and stereospecific
What Are Elimination Reaction Give Example
 What Are Elimination Reaction Give Example
What Are Elimination Reaction Give Example
https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eliminationreaction1-180823164955/95/elimination-reaction-1-1024.jpg?cb=1535043410
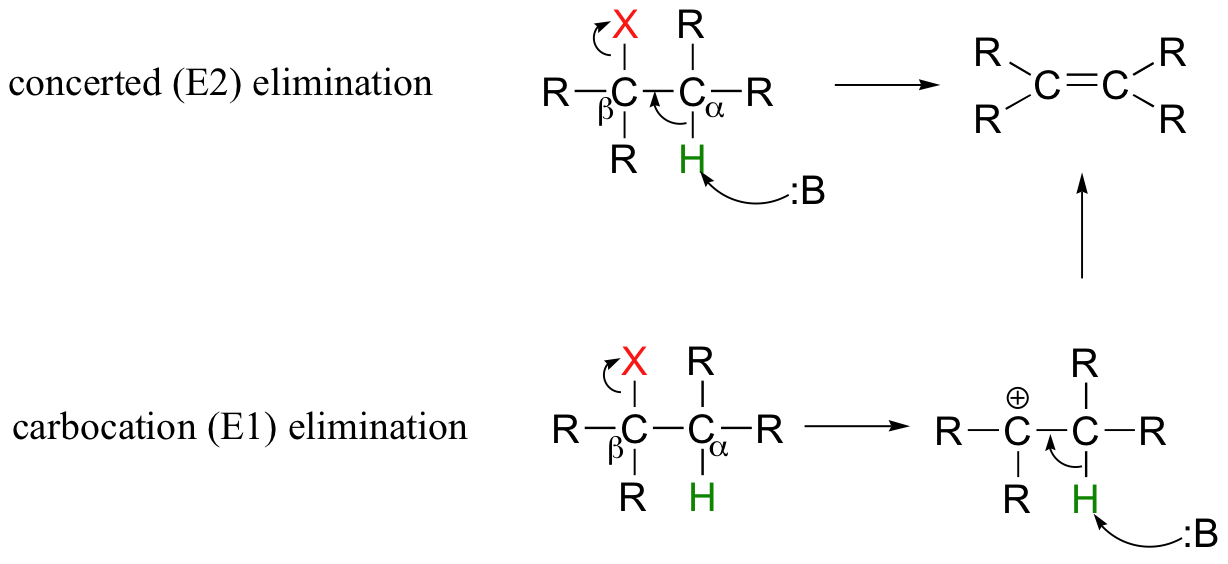
Elimination vs substitution tertiary substrate Sn1 Sn2 E1 and E2 reactions form the basis for understanding why certain products are more likely to form than others We will learn about the reaction mechanisms and how nucleophilicity and electrophilicity can be used to choose between different reaction pathways
Templates are pre-designed files or files that can be used for numerous functions. They can conserve time and effort by supplying a ready-made format and layout for producing different sort of content. Templates can be used for personal or expert tasks, such as resumes, invites, leaflets, newsletters, reports, discussions, and more.
What Are Elimination Reaction Give Example
7 18 Comparaci n De Las Reacciones E1 Y E2 LibreTexts Espa ol
Formic acid ir

8 5 Elimination Reactions Organic Chemistry 1 An Open Textbook
Elimination Method For Systems Of Equations
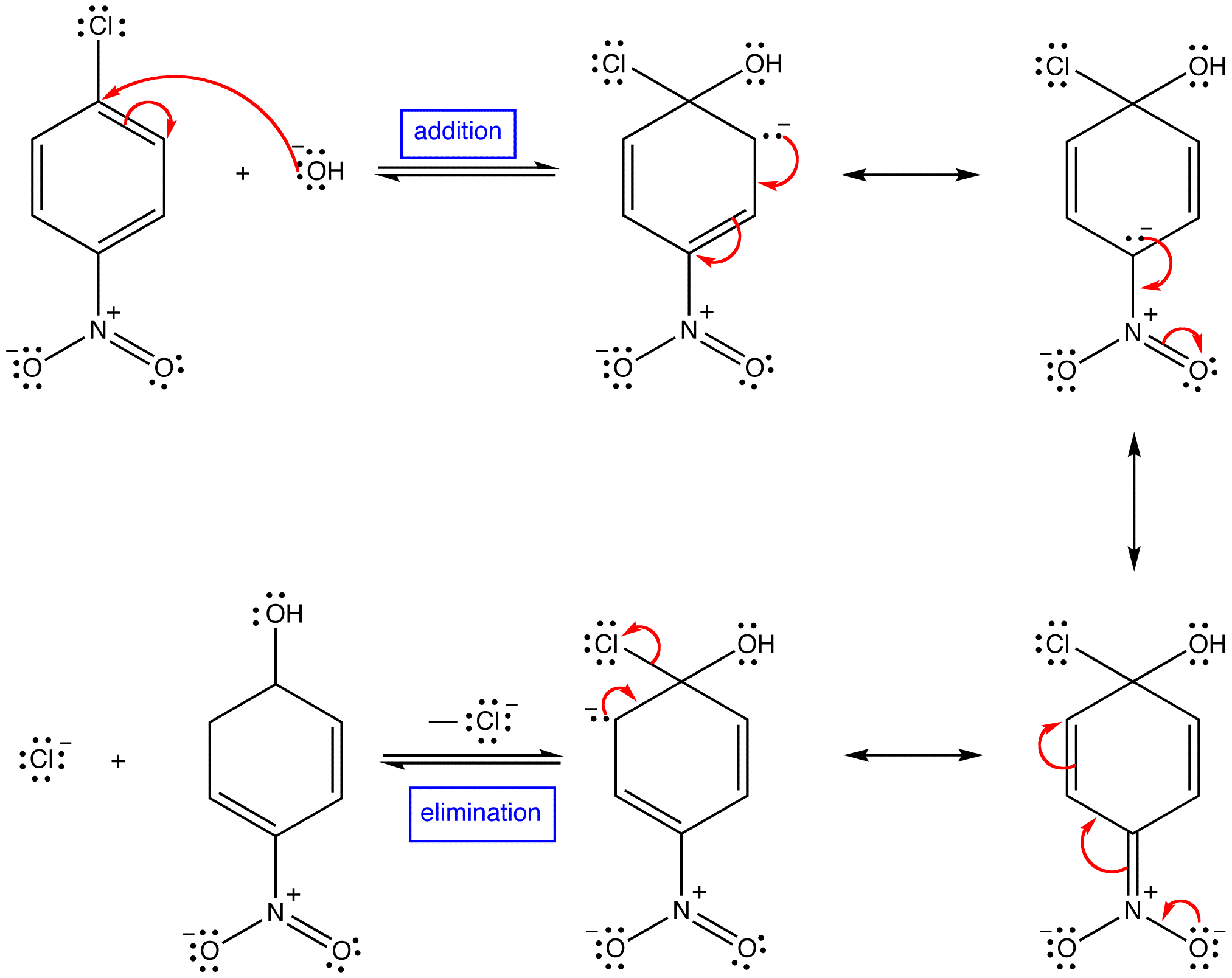
Addition Elimination Mechanism Chemistry LibreTexts
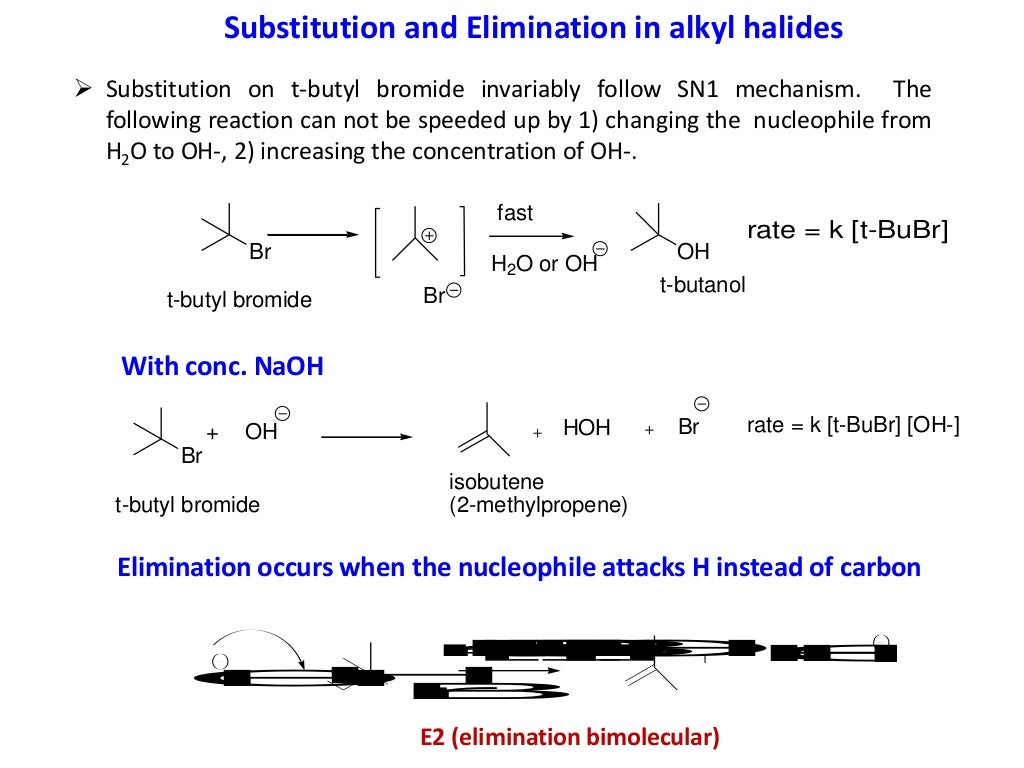
Elimination Reaction

https://www.chemistrylearner.com/elimination-reaction.html
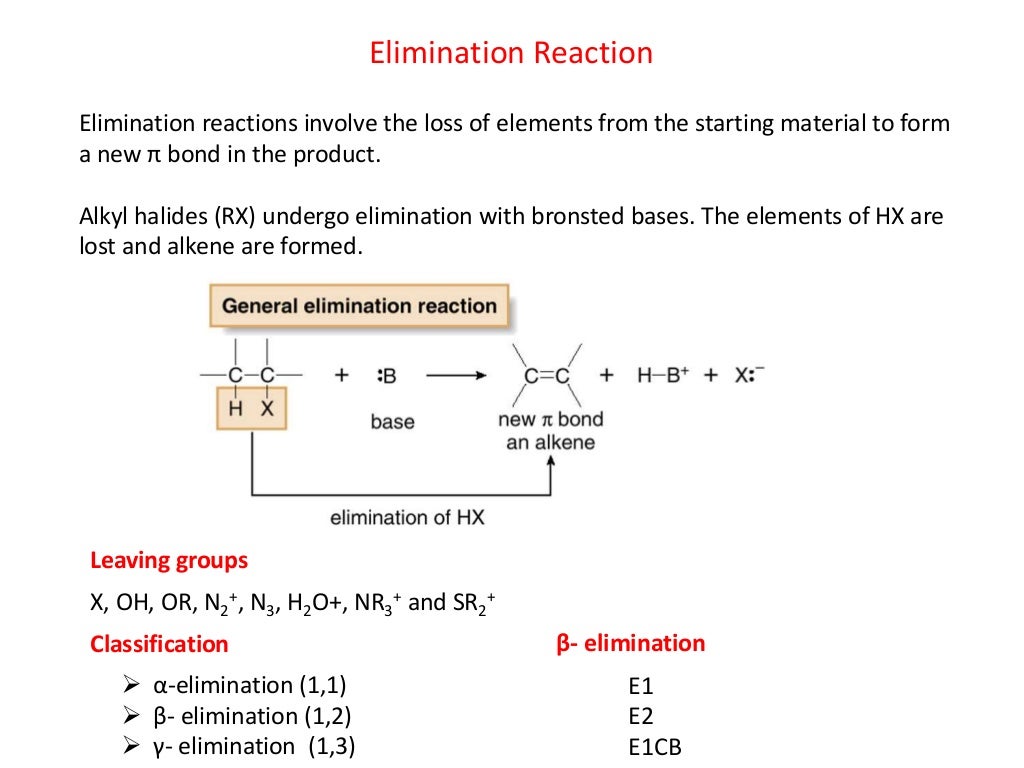
The elimination reaction is an organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule to form a new product The process takes place in the presence of acid base metal and sometimes through heating

https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/SUNY_Potsdam
In order to direct the reaction towards elimination rather than substitution heat is often used This is because elimination leads to an increase in the number of molecules from two to three in the above example and thus an increase in entropy High temperatures favor reactions of this sort where there is a large increase in entropy

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Elimination_reaction
An example of this type of reaction in scheme 1 is the reaction of isobutylbromide with potassium ethoxide in ethanol The reaction products are isobutene ethanol and potassium bromide E1 mechanism E1 is a model to explain a

https://www.britannica.com/science/elimination-reaction
Elimination reactions are commonly known by the kind of atoms or groups of atoms leaving the molecule The removal of a hydrogen atom and a halogen atom for example is known as dehydrohalogenation when both leaving atoms are halogens the reaction is known as dehalogenation
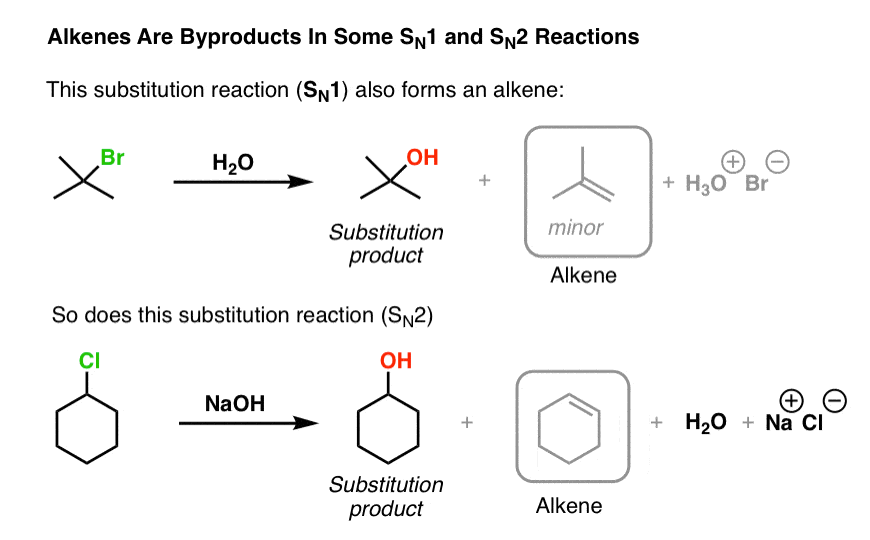
https://www.vedantu.com/chemistry/elimination-reaction
4 days ago 0183 32 What is Elimination Reaction An elimination reaction is a type of organic reaction in which two substituents are removed from a molecule in either a one or two step mechanism Examples are given below images will be uploaded soon Important Methods of Elimination Reaction
In an elimination reaction a small molecule XY is removed from two adjacent atoms of the reactant and a multiple bond is formed in the product Figure 8 0a General equation of elimination reaction For an elimination reaction of alkyl halides the major product alkene is produced together with the small HX X is halogen molecule which is Truong Son N Nov 17 2015 In general an elimination reaction specifically it s called elimination involves the elimination of a proton from the carbon forming a bond and ejecting a leaving group Note that they don t necessarily
Unit 1 Electrophilic addition reactions of alkenes and alkynes Unit 2 Electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions Unit 3 Nucleophilic substitution reactions of alkyl halides alcohols and ethers Unit 4 Elimination reactions haloalkanes Unit 5 Nucleophilic addition reactions of aldehydes and ketones