What Is The Mean Value Theorem WEB The mean value theorem MVT also known as Lagrange s mean value theorem LMVT provides a formal framework for a fairly intuitive statement relating change in a function to the behavior of its derivative
WEB What is the mean value theorem The mean value theorem connects the average rate of change of a function to its derivative It says that for any differentiable function f and an interval a b within the domain of f there exists a number c within a b such that f c is equal to the function s average rate of change over a b WEB Aug 29 2023 0183 32 The Mean Value Theorem says that the derivative of a differentiable function will always attain one particular value on a closed interval the function s average rate of change over the interval It turns out that the derivative will take on every value between its values at the endpoints similar to how the Intermediate Value Theorem
What Is The Mean Value Theorem
 What Is The Mean Value Theorem
What Is The Mean Value Theorem
https://image3.slideserve.com/6576227/mean-value-theorem-l.jpg
WEB The Mean Value Theorem Learning Objectives Explain the meaning of Rolle s theorem Describe the significance of the Mean Value Theorem State three important consequences of the Mean Value Theorem The Mean Value Theorem is one of the most important theorems in calculus We look at some of its implications at the end of this section
Pre-crafted templates offer a time-saving solution for developing a varied range of documents and files. These pre-designed formats and designs can be used for various individual and expert projects, including resumes, invites, flyers, newsletters, reports, presentations, and more, simplifying the content development procedure.
What Is The Mean Value Theorem
PPT The Mean Value Theorem PowerPoint Presentation Free Download
Mean Value Theorem
PPT 3 2 Rolle s Theorem And The Mean Value Theorem PowerPoint

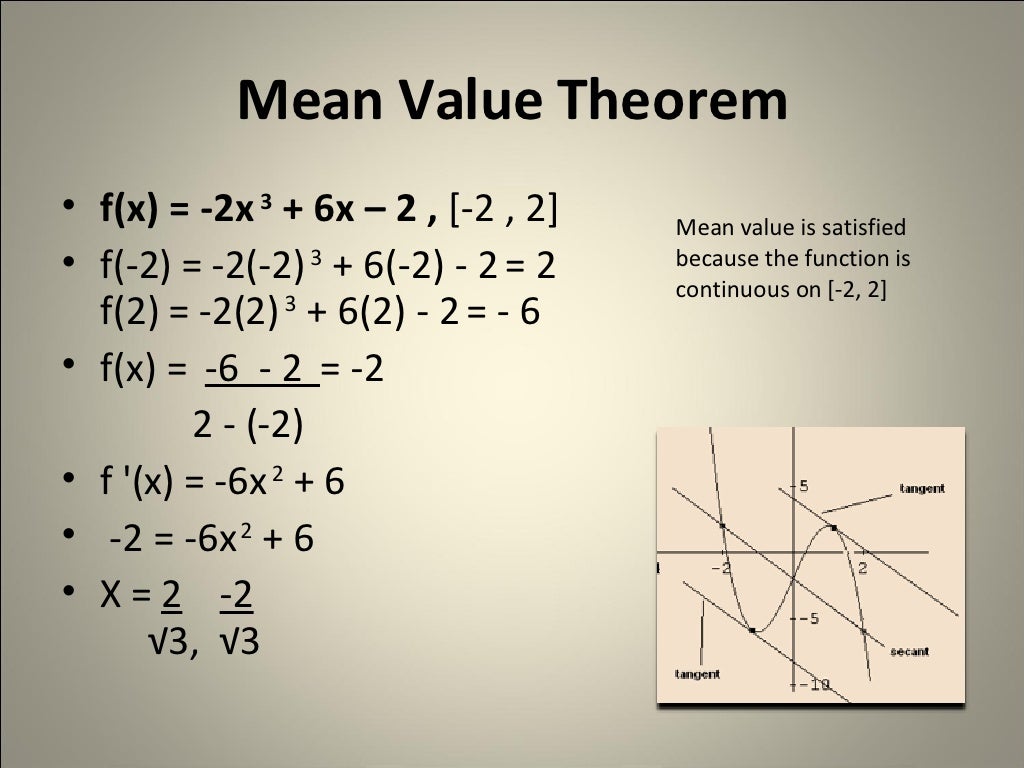
Mean Value Theorem Example YouTube
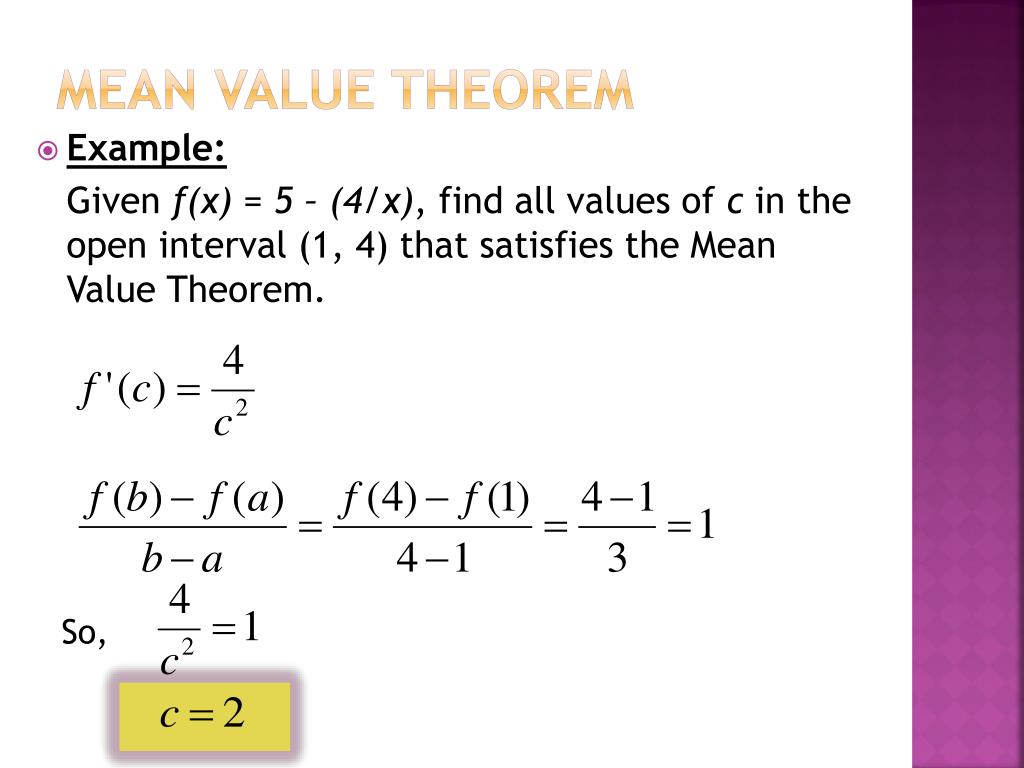
PPT 4 2 Mean Value Theorem PowerPoint Presentation Free Download
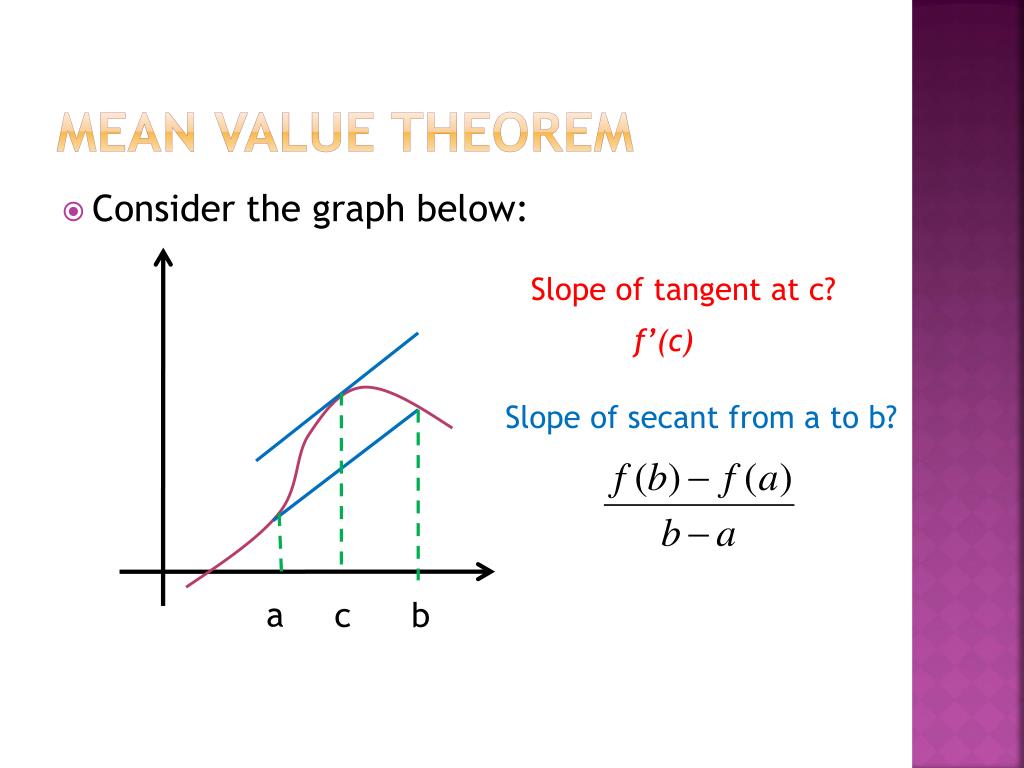
PPT 4 2 Mean Value Theorem PowerPoint Presentation Free Download

https://openstax.org//4-4-the-mean-value-theorem
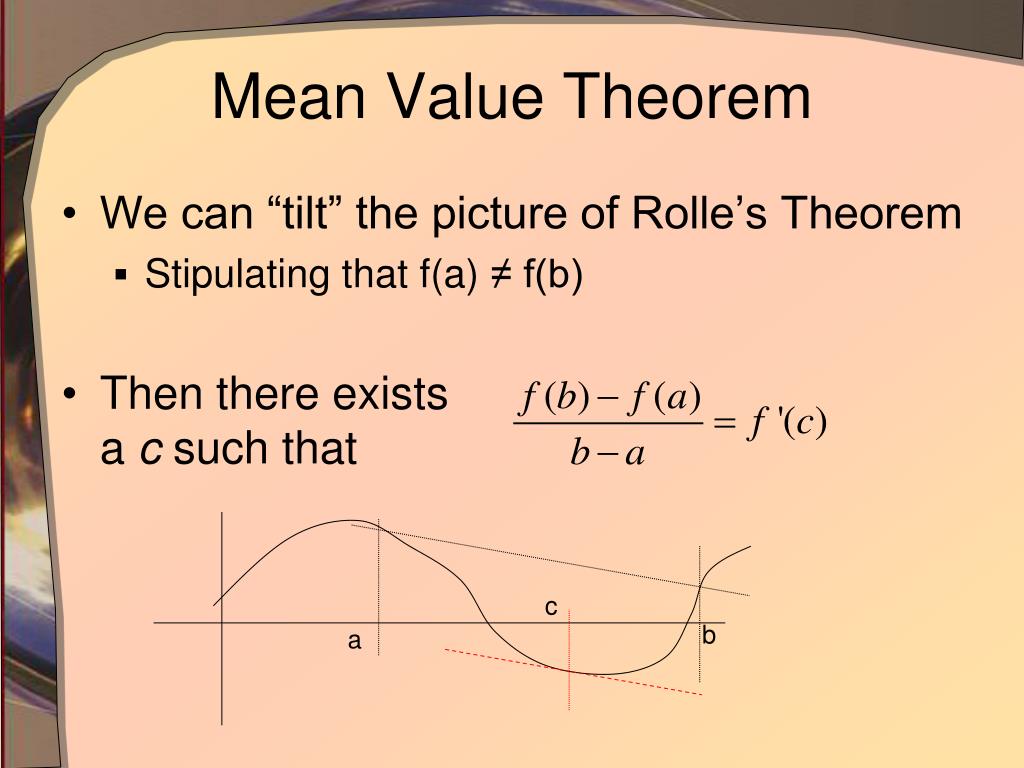
WEB The Mean Value Theorem generalizes Rolle s theorem by considering functions that do not necessarily have equal value at the endpoints Consequently we can view the Mean Value Theorem as a slanted version of Rolle s theorem Figure 4 25

https://tutorial.math.lamar.edu/Classes/CalcI/MeanValueTheorem.aspx
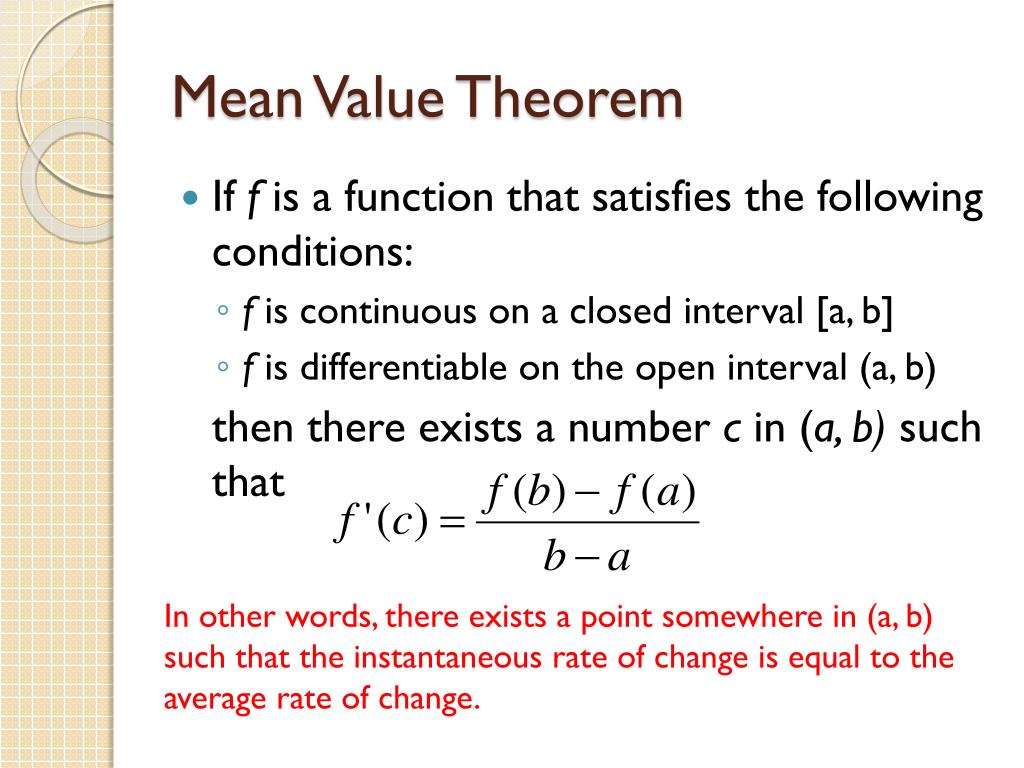
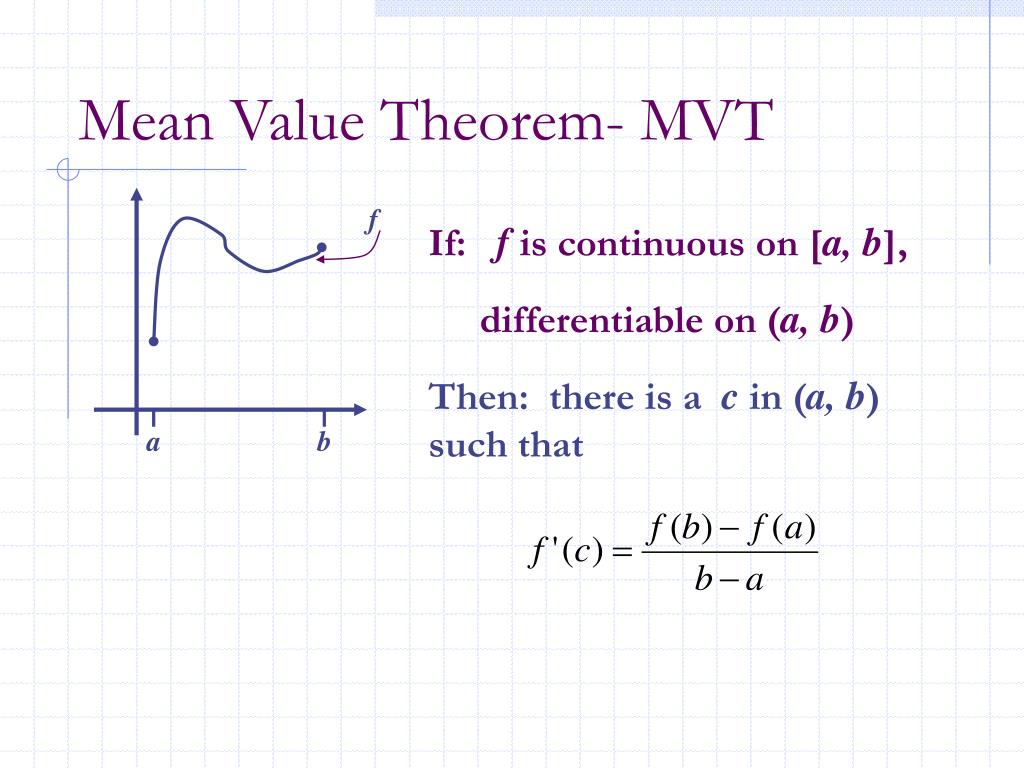
WEB Nov 16 2022 0183 32 Mean Value Theorem Suppose f x f x is a function that satisfies both of the following f x f x is continuous on the closed interval a b a b f x f x is differentiable on the open interval a b a b Then there is a number c c such that a lt c lt b and f c f b f a b a f c f b f a b a Or

https://www.khanacademy.org//ab-5-1/v/mean-value-theorem-1
WEB The Mean Value Theorem states that if a function f is continuous on the closed interval a b and differentiable on the open interval a b then there exists a point c in the interval a b such that f c is equal to the function s average rate of change over a b
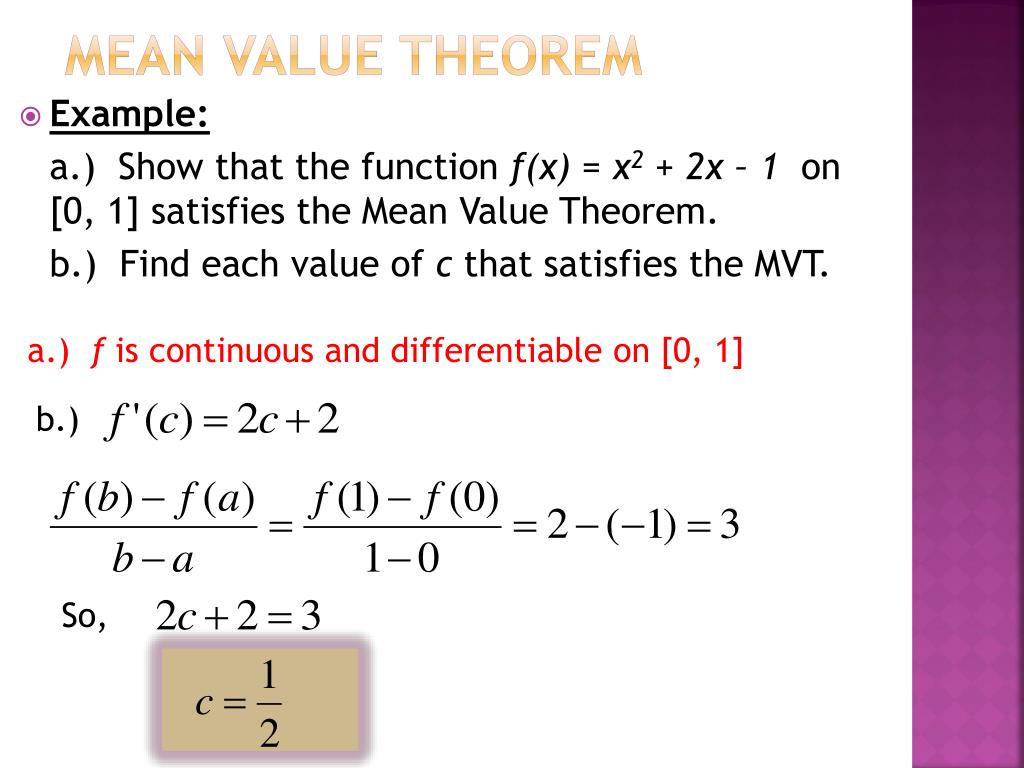
https://www.cuemath.com/calculus/mean-value-theorem
WEB The mean value theorem states that the slope of the secant joining any two points on the curve is equal to the slope of the tangent at a point that lies between the given two points Learn to apply the mean value theorem Also check examples and FAQs

https://math.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Calculus
WEB Nov 10 2020 0183 32 The Mean Value Theorem states that if f is continuous over the closed interval a b and differentiable over the open interval a b then there exists a point c a b such that the tangent line to the graph of f at c is parallel to the secant line connecting a f a and b f b
[desc-11] [desc-12]
[desc-13]