What Are The 13 Parts Of A Plant Cell Plant Cells Plant Cell Components Cell Wall Plasma Membrane and Middle Lamella The Nucleus Plastids Chloroplasts Chromoplasts Leucoplasts The Central Vacuole
The plant cell has a cell wall chloroplasts plastids and a central vacuole structures not in animal cells Most cells do not have lysosomes or centrosomes The Plasma Membrane Jan 17 2020 0183 32 Plant Cell Structure and Function Even though cells differ in size and complexity they contain many of the same substances and they carry out similar life functions These include growth metabolism and reproduction Cells are made up of different structures that are responsible for specific functions
What Are The 13 Parts Of A Plant Cell
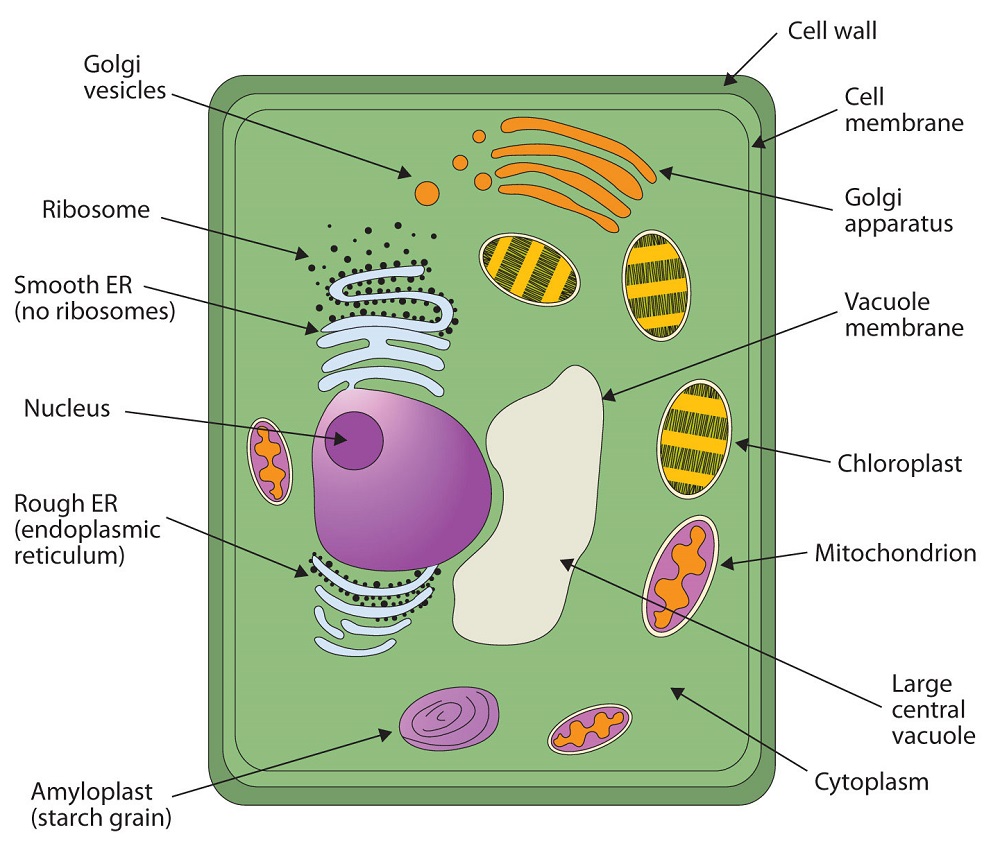 What Are The 13 Parts Of A Plant Cell
What Are The 13 Parts Of A Plant Cell
https://www.winkelhage.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/Plant-Cell.jpg
Plant cells have a cell wall a large central vacuole and plastids such as chloroplasts The cell wall is a rigid layer that is found outside the cell membrane and surrounds the cell providing structural support and protection
Pre-crafted templates use a time-saving option for producing a varied variety of documents and files. These pre-designed formats and designs can be made use of for numerous personal and professional jobs, including resumes, invitations, leaflets, newsletters, reports, presentations, and more, enhancing the material development procedure.
What Are The 13 Parts Of A Plant Cell

Diagram Of Plant Cell

Plant Cell Diagram Quizlet

13 Best Images Of Parts Of A Plant Cell Worksheet Plant Cell Structure

Structure Of A Plant Cell Learning Science Plant Cell Classical
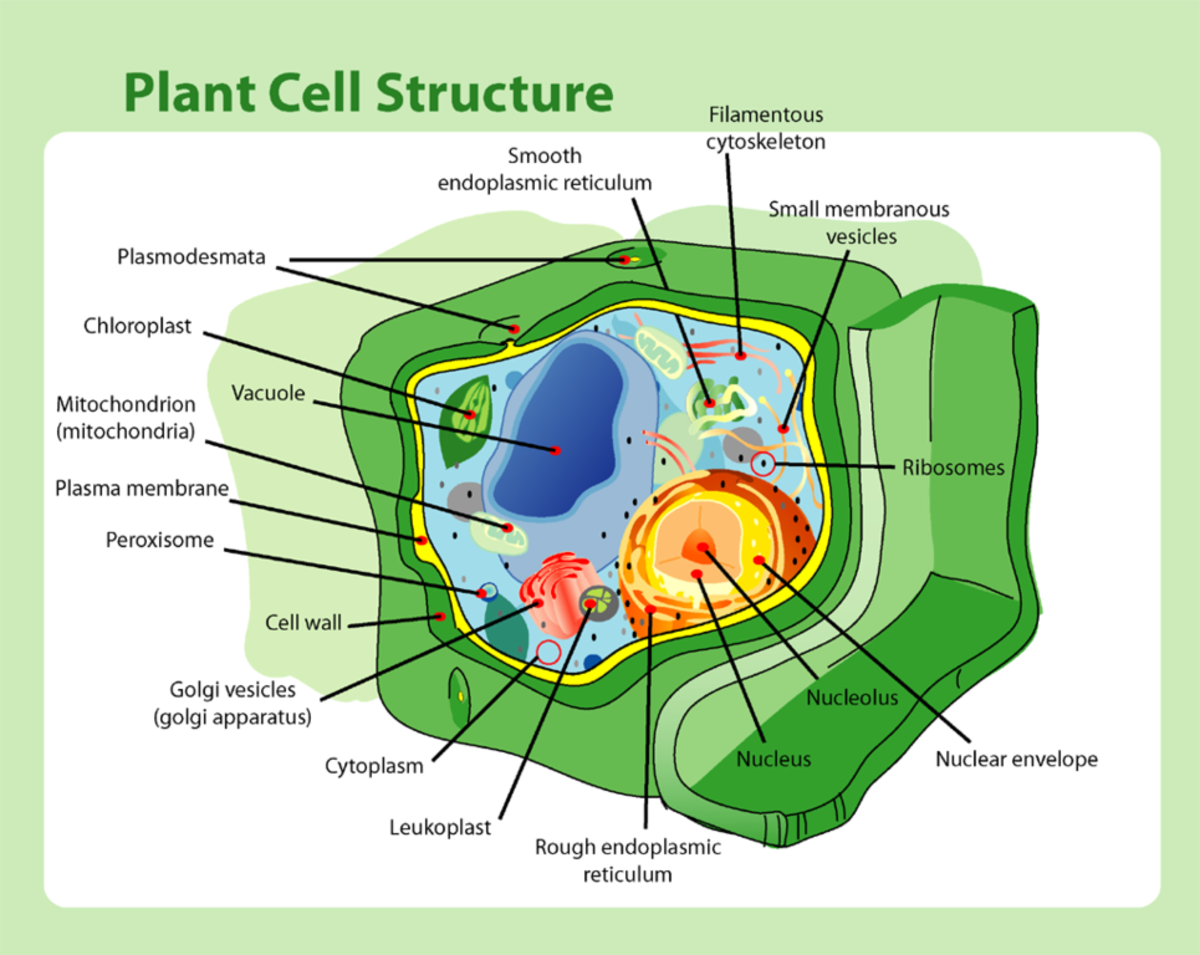
Plant Cell Its 6 Main Parts And Their Functions HubPages

Plant cell diagram Tim s Printables
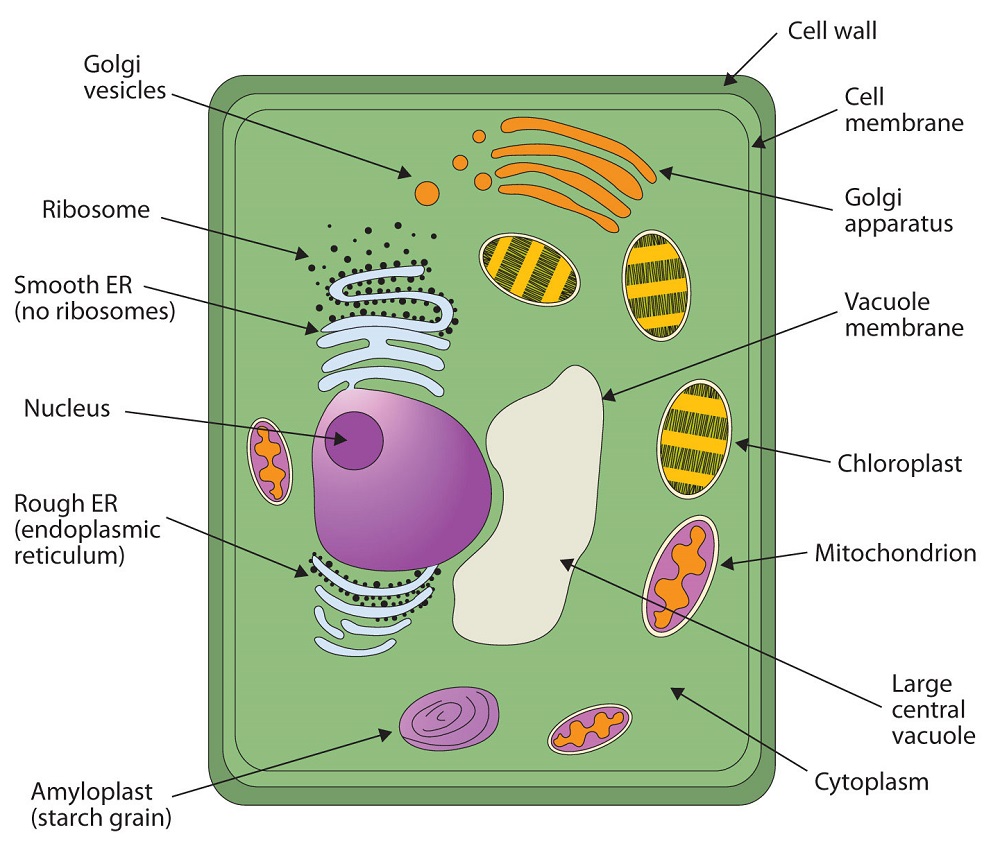
https://sciencenotes.org/plant-cell-diagram-organelles-and-characteristics
May 17 2023 0183 32 A plant cell is the basic building block of a plant Plant cells like all eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and other organelles each with its distinct functions However plant cells also possess unique components that differentiate them from animal fungal and bacterial cells Plant Cell Characteristics Plant cells are eukaryotic

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Plant_cell
Plant cells differentiate from undifferentiated meristematic cells analogous to the stem cells of animals to form the major classes of cells and tissues of roots stems leaves flowers and reproductive structures each of which may

https://biologydictionary.net/plant-cell
Jan 15 2021 0183 32 Plant cells are differentiated from the cells of other organisms by their cell walls chloroplasts and central vacuole Chloroplasts are organelles that are crucial for plant cell function These are the structures that carry out photosynthesis using the energy from the sun to produce glucose

https://www.britannica.com/science/plant-cell
plant cell the basic unit of all plants Plant cells like animal cells are eukaryotic meaning they have a membrane bound nucleus and organelles The following is a brief survey of some of the major characteristics of plant cells For

https://www.sciencefacts.net/plant-cell.html
Oct 21 2021 0183 32 Different Parts of a Plant Cell Plant Cell Diagram 1 Cell Wall It is the outermost protective layer of a plant cell having a thickness of 20 80 nm Cell walls are made up of carbohydrates such as cellulose hemicellulose and pectin and a complex organic polymer called lignin Functions
Jan 5 2024 0183 32 Parts of Plant Cells Like animal cells plant cell consist of cell membrane cytoplasm nucleus vacuoles cell organelles like endoplasmic reticulum ribosomes and mitochondria Besides these parts plant cells have Sep 16 2023 0183 32 Cytoplasm Plastids Development of plastids General functions of plastids Types of Plastids Chloroplast Structure of the plant cell chloroplast Functions of the plant cell chloroplast Chromoplast plastid Structure of plant chromoplast Functions of plant chromoplast Gerontoplast plastids of the plant cell Leucoplast plastids of the plant cell
This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below the same plant cell as viewed with the light microscope and with the transmission electron microscope